Home > Blog > Balance your health with Ayurveda > Causes and Treatment of Gout with Ayurveda
Causes and Treatment of Gout with Ayurveda
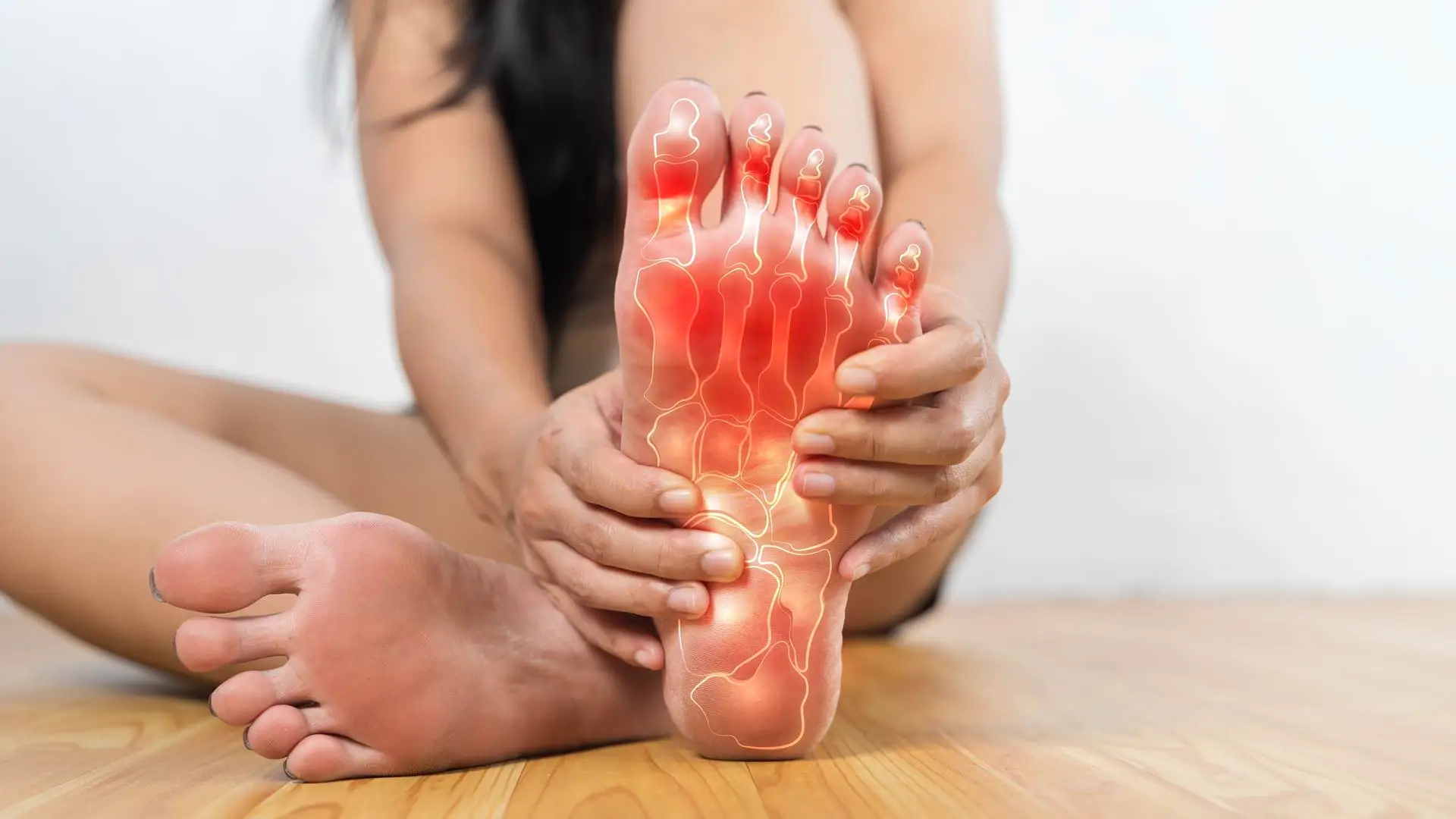
Gout (also called metabolic arthritis and known to Ayurveda as Vatarakta) is a disease due to a disorder of uric acid metabolism in the blood.
In this condition, monosodium urate or uric acid crystals are deposited on the articular cartilage of joints, tendons and surrounding tissues due to elevated concentrations of uric acid in the blood stream.
This provokes an inflammatory reaction of these tissues.
These deposits can often increase in size and burst through the skin to form sinuses discharging a chalky white material.
The classic picture is of excruciating, sudden, unexpected, burning pain, swelling, redness, warmness and stiffness in the joint. Low-grade fever may also be present. The patient usually suffers from two sources of pain: firstly, the crystals inside the joint cause intense pain whenever the affected area is moved. Secondly, the inflammation of the tissues around the joint also causes the skin to be swollen, tender and sore if it is even slightly touched. For example, a blanket or even the lightest sheet draping over the affected area could cause extreme pain.

